In a world where fast fashion dominates wardrobes and supply chains, a growing movement is redefining what it means to dress well. Fair trade fashion stands at the intersection of ethics, sustainability, and style — ensuring that the clothes we wear are not only beautiful but also responsibly made.
By prioritizing fair wages, safe working conditions, and environmentally conscious production, fair trade fashion promotes equality and respect for both people and the planet. As consumers become more aware of where their clothes come from, fair trade principles are leading a quiet revolution in how we view fashion’s true value.
What Is Fair Trade Fashion?
Fair trade fashion is an ethical approach to clothing production that ensures every person involved in the supply chain is treated fairly and paid justly. It prioritizes transparency, human rights, and environmental protection.
In simple terms, fair trade means that artisans, farmers, and workers receive fair compensation for their labor and materials — allowing them to live with dignity while preserving traditional skills and sustainable practices.
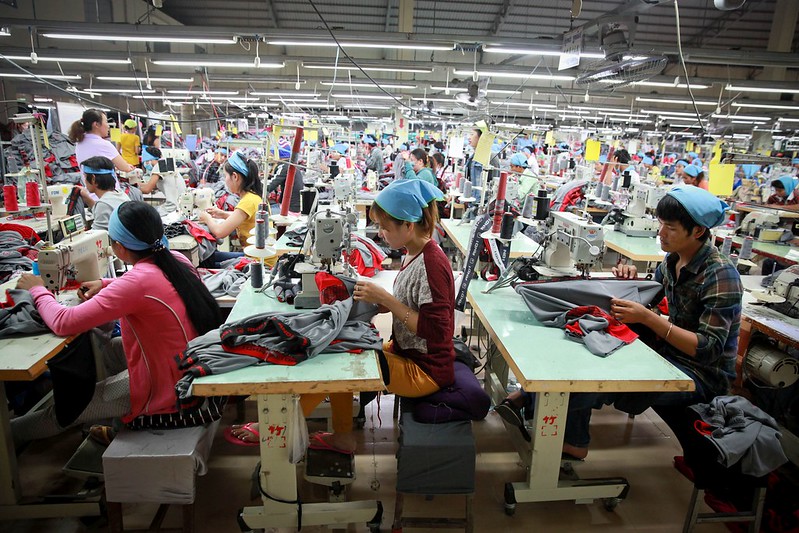
This model challenges the exploitative systems of fast fashion, where low-cost, high-speed production often comes at the expense of workers’ safety and the environment.
The Core Principles of Fair Trade Fashion
Fair trade fashion is built on several guiding principles that ensure ethical integrity from start to finish:
- Fair Wages – Workers are paid a living wage that covers food, housing, education, and healthcare.
- Safe Working Conditions – Factories and workshops must comply with health and safety standards.
- Empowerment of Women and Communities – Many fair trade initiatives support women-led cooperatives and local artisans.
- Environmental Sustainability – Eco-friendly materials and low-impact production reduce pollution and waste.
- Transparency and Traceability – Brands must disclose their sourcing and manufacturing processes.
- Cultural Preservation – Traditional craftsmanship is valued and promoted over mass-produced trends.
Together, these principles create a supply chain rooted in respect and sustainability — proving that fashion can be both ethical and aspirational.
Why Fair Trade Fashion Matters
The global fashion industry employs over 75 million people, yet many garment workers earn less than a living wage. Factories in developing countries often cut corners on safety and environmental standards to meet the demands of fast, cheap production.
Fair trade fashion provides an alternative that prioritizes humanity over profit. By supporting ethical brands, consumers help fund education, healthcare, and community development in producer regions.
Moreover, fair trade encourages sustainable farming of materials like organic cotton, hemp, and bamboo — reducing water consumption and chemical pollution.
Fair Trade vs. Fast Fashion: A Clear Contrast
| Feature | Fair Trade Fashion | Fast Fashion |
|---|---|---|
| Worker Treatment | Fair wages, safe conditions | Low pay, often unsafe conditions |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly materials, reduced waste | High pollution, resource depletion |
| Production Speed | Small-scale, ethical manufacturing | Mass-produced at high speed |
| Transparency | Full supply chain visibility | Often lacks transparency |
| Design Philosophy | Timeless, culturally inspired | Trend-driven, short-lived styles |
| Consumer Role | Conscious, mindful shopper | Impulsive, trend-focused buyer |
Fair trade fashion invites us to slow down, think critically, and make choices that align with our values.
The Rise of Fair Trade Fashion Brands
As demand for ethical products grows, a new wave of fair trade-certified brands is leading the charge. Some notable examples include:
- People Tree (UK): One of the pioneers of fair trade clothing, known for sustainable fabrics and artisanal craftsmanship.
- Mata Traders (USA): Partners with women-led cooperatives in India and Nepal to create handmade, vibrant apparel.
- Patagonia: A global leader in sustainable outdoor wear with transparent supply chain practices.
- Suku Home (Australia): Focuses on artisanal, handmade textiles and ethical labor practices.
These brands prove that fair trade can coexist with creativity and style — offering everything from classic staples to contemporary designs.
How Fair Trade Fashion Encourages Conscious Consumption
When you buy a fair trade item, you’re not just purchasing a garment — you’re making a statement about the kind of world you want to support.
Fair trade fashion embodies purposeful consumption. It’s about valuing craftsmanship over convenience, quality over quantity, and sustainability over speed.
This mindset also aligns with Self-Expression Dressing, a concept that emphasizes wearing clothes that reflect personal identity and values. When consumers choose fair trade garments, they express more than style — they communicate empathy, awareness, and respect for global communities.
In this sense, ethical clothing becomes not only an aesthetic choice but also a form of empowerment and authenticity.
Materials Commonly Used in Fair Trade Fashion
| Material | Sustainable Advantage | Common Use |
|---|---|---|
| Organic Cotton | Grown without harmful chemicals | T-shirts, dresses, basics |
| Hemp | Requires minimal water and pesticides | Pants, outerwear, accessories |
| Bamboo | Naturally antibacterial and renewable | Activewear, loungewear |
| Tencel (Lyocell) | Made from sustainably sourced wood pulp | Blouses, dresses |
| Recycled Fabrics | Reduces landfill waste | Jackets, bags, shoes |
By focusing on renewable and biodegradable materials, fair trade fashion reduces the industry’s carbon footprint and extends product life cycles.
How to Identify Genuine Fair Trade Brands
As “greenwashing” becomes more common, it’s important to distinguish true fair trade brands from those that merely claim sustainability.
Look for the following certifications or indicators:
- Fair Trade Certified™
- World Fair Trade Organization (WFTO)
- Global Organic Textile Standard (GOTS)
- B Corp Certification
- Transparent supply chain reporting on brand websites
Authentic fair trade companies are transparent about their practices, often sharing detailed information about their suppliers and production facilities.
Benefits of Supporting Fair Trade Fashion
- Empowers Artisans and Workers: Ensures fair pay, education, and community growth.
- Reduces Environmental Harm: Encourages sustainable production and material sourcing.
- Promotes Cultural Heritage: Keeps traditional techniques alive through global markets.
- Builds Consumer Awareness: Encourages thoughtful purchasing and waste reduction.
- Improves Product Longevity: Higher-quality garments last longer, reducing replacement costs.
Each purchase is a small step toward a more ethical and environmentally balanced fashion industry.
The Future of Fair Trade Fashion
As the demand for transparency and sustainability rises, fair trade fashion is poised to become a cornerstone of the modern fashion economy.
Brands are increasingly adopting circular production models, focusing on recycling, upcycling, and reusing materials. Digital technologies are also enabling traceable supply chains, allowing customers to follow their garments’ journey from raw material to final product.
With continued consumer advocacy, fair trade fashion can push the industry toward genuine sustainability — creating a world where looking good and doing good go hand in hand.
FAQs About Fair Trade Fashion
Q1. Is fair trade fashion affordable?
While it often costs more than fast fashion, the investment reflects fair wages, sustainable materials, and higher quality — offering better long-term value.
Q2. Where can I buy fair trade clothing?
Many ethical brands sell online through their websites or marketplaces like Made Trade, EarthHero, and Etsy Fair Trade shops.
Q3. Are all sustainable brands fair trade certified?
No. While both emphasize ethics and sustainability, only certified brands guarantee fair labor and pricing standards.
Q4. How does fair trade affect local communities?
It provides financial stability, education opportunities, and empowerment for workers, especially women in developing countries.
Q5. Can fair trade apply to luxury fashion?
Yes. Many luxury designers are adopting fair trade sourcing, proving that ethics and elegance can coexist.
Final Thoughts
Fair trade fashion represents more than an ethical choice — it’s a commitment to fairness, transparency, and sustainability in an industry long dominated by exploitation. It reminds us that fashion can be a tool for positive change rather than harm.
By choosing fair trade garments, consumers join a global movement toward conscious consumption, environmental stewardship, and respect for humanity. In the end, dressing ethically isn’t just about what we wear — it’s about what we stand for.